1. What type of color Doppler mapping displays a combination of primary colors?
a. hue
b. mosaic
c. variance
d. saturation
2. Thickening of the spectral trace is most likely a result of:
a. the reverberation artifact
b. low-amplitude Doppler shifts
c. an increase in the range of Doppler shift frequencies
d. the quantity of blood moving through the sample volume 3. This spectral thickening is termed:
a. clutter
b. aliasing
c. saturation
d. spectral broadening
4. The size of the sample volume is determined by the beam diameter, length of the ultrasound pulse, and:
a. Doppler shift
b. Doppler angle
c. operating frequency
d. receiver gate length
5. Which of the following converts Doppler shift information into a visual spectral display?
a. scan converter
b. autocorrelation
c. fast Fourier transform
d. digital–analog converter
6. In color-flow Doppler, multiple sample gates positioned in the area of interest are termed:
a. pixels
b. voxels
c. packets
d. color volumes
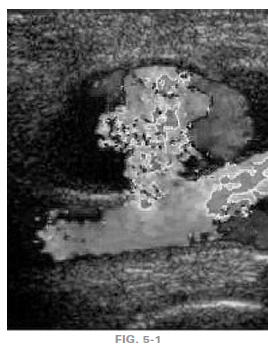
7. Which of the following changes will improve this color Doppler image?
a. raise color baseline
b. decrease color gain
c. increase color scale
d. change acoustic window
8. Which of the following correctly describes the hemodynamics of blood flow?
a. Blood only flows when pressures are equal
b. Blood flows from low pressure to high pressure
c. Blood flows from higher pressure to lower pressure
d. Blood flows from higher velocity to lower velocity
9. Increasing the operating frequency will:
a. overcome aliasing
b. increase the packet size
c. increase the Nyquist limit
d. increase sensitivity to low Doppler shifts
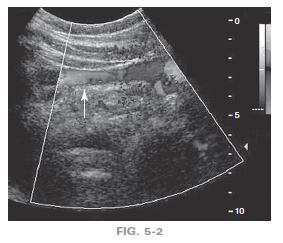
10. Which of the following changes will improve this color Doppler image?
a. decrease color scale
b. decrease color gain
c. decrease imaging depth
d. decrease operating frequency
11. The greater the pressure gradient, the greater the:
a. flow velocity
b. flow resistance
c. Reynolds number
d. blood flow volume
12. Resistance to blood flow is proportional to the
a. flow velocity
b. Reynolds number
c. blood flow volume
d. length of the vessel

