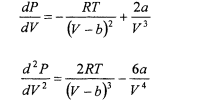The van der Waals equation is an equation of state that applies to real gases. For 1 mole of a gas, the van der Waals equation is
![]()
where R is the gas constant (0.0821 L atm K-‘ mol-‘) and T is the Kelvin temperature. The constants a and b are constants particular to a given gas, and correct for the attractive forces between gas molecules, and for the volume occupied by the gas molecules, respectively. For methane (CK), the constants are a = 2.253 L2 atm and b = 4.278 x L. Using the rearranged form of the van der Waals equation
![]()
calculate the pressure of 1 mole of methane as a function of container volume at 0°C (273 K) at suitable volumes from 22.4 L to 0.05 L. Use one of the custom functions described in this chapter to calculate the first and second derivatives of the P-V relationship. Compare with the exact expressions