1.In a reciprocating pump without air vessels, the friction head in the delivery
pipe is maximum at crank angle q =
(a) 0° (b) 90° (c) 60° (d) 180°
2. * In a reciprocating pump without air vessels, the acceleration head in the
suction pipe is maximum at the crank angle value of q =
(a) 0° (b) 90° (c) 60° (d) 180°
3. The indicator diagram of a reciprocating pump is a plot of
(a) work done vs stroke length
(b) acceleration head vs stroke length
(c) pressure head vs stroke length
(d) crank speed vs power developed
4. A double-stoke reciprocating pump has its stroke length reduced by half and
the speed is doubled. This would cause the discharge to
(a) decrease by 25% (b) remain unaltered
(c) decrease by 50% (d) increase by 100%
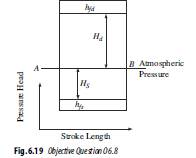
5. Figure 6.19 shows an indicator diagram of a single-acting reciprocating pump. This indictor diagram belongs to
(a) a reciprocating pump with two air vessels, one each in suction pipe and
delivery pipe at some distance from the cylinder
(b) a reciprocating pump with one air vessel
(c) a reciprocating pump with two ideal air vessels
(d) a reciprocating pump with no air vessels