Rob Otics Ltd, a small business that specialises in building electronic-control equipment, has
just received an order from a customer for eight identical robotic units. These will be completed
using Rob Otics’s own labour force and factory capacity. The product specification prepared by
the estimating department shows the following material and labour requirements for each
robotic unit:
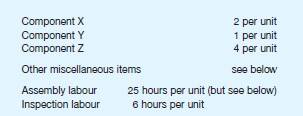
As part of the costing exercise, the business has collected the following information:
l Component X. This item is normally held by the business as it is in constant demand. The 10
units currently held were invoiced to Rob Otics at £150 a unit, but the sole supplier has
announced a price rise of 20 per cent effective immediately. Rob Otics has not yet paid for
the items currently held.
l Component Y. 25 units are currently held. This component is not normally used by Rob Otics
but the units currently held are because of a cancelled order following the bankruptcy of a
customer. The units originally cost the business £4,000 in total, although Rob Otics has
recouped £1,500 from the liquidator of the bankrupt business. As Rob Otics can see no use
for these units (apart from the possible use of some of them in the order now being considered),
the finance director proposes to scrap all 25 units (zero proceeds).
l Component Z. This is in regular use by Rob Otics. There is none in inventories but an order
is about to be sent to a supplier for 75 units, irrespective of this new proposal. The supplier
charges £25 a unit on small orders but will reduce the price to £20 a unit for all units on any
order over 100 units.
l Other miscellaneous items. These are expected to cost £250 in total.
Assembly labour is currently in short supply in the area and is paid at £10 an hour. If the order
is accepted, all necessary labour will have to be transferred from existing work, and other orders
will be lost. It is estimated that for each hour transferred to this contract £38 will be lost (calculated
as lost sales revenue £60, less materials £12 and labour £10). The production director
suggests that, owing to a learning process, the time taken to make each unit will reduce, from
25 hours to make the first one, by one hour a unit made.
Inspection labour can be provided by paying existing personnel overtime which is at a premium
of 50 per cent over the standard rate of £12 an hour.
When the business is working out its contract prices, it normally adds an amount equal to
£20 for each assembly hour to cover its general costs (such as rent and electricity). To the
resulting total, 40 per cent is normally added as a profit mark-up.
Required:
(a) Prepare an estimate of the minimum price that you would recommend Rob Otics Ltd to
charge for the proposed contract such that it would be neither better nor worse off as a
result. Provide explanations for any items included.
(b) Identify any other factors that you would consider before fixing the final price.

