Terminology. Please match each item on the left with the most appropriate item on the
right.
| 1. Authorize a purchase
2. Bank reconciliation 3. Purchase order 4. Purchase requisition 5. Quantity discounts 6. Receiving report 7. Reorder point 8. Source documents, journal entries, ledger postings 9. Strategic alliance 10. Vendor invoice |
a. A way to monitor inventory needs.
b. Audit trail components. c. Internal control to manage the risk of embezzlement. d. One reason for consolidating purchase requisitions. e. Possible internal control for purchasing from inappropriate vendors. f. Prepared by purchasing department. g. Promotes separation of duties. h. Requests customer payment. i. Several can be combined on one purchase order. j. Step in the acquisition/payment process. |
221. PLP Corporation maintains an electronic database file for all its vendors and purchases. Which of the following amounts would you be least likely to find in the “vendor” table
a. Total amount owed
b. Vendor name
c. Part numbers commonly purchased
d. All of the above would be included in the vendor table.
222. An accounting clerk debited inventory and credited accounts payable for $500. Which of
the following is the most likely source document for that transaction?
a. Purchase order
b. Receiving report
c. Vendor invoice
d. Purchase requisition
223. In the context of an acquisition/payment process, the three-way match concept applies to
which of the following sets of documents?
a. Purchase requisition, vendor invoice, and remittance advice
b. Vendor invoice, receiving report, and purchase requisition
c. Receiving report, purchase order, and vendor invoice
d. Remittance advice, purchase order, and receiving report
224. Although the ideas associated with the acquisition/payment process are most commonly
associated with , they also can be applied to .
a. Sales, purchases
b. Purchases, sales
c. Inventory, other assets
d. Supplies, intangibles
225. Which of the following steps in the acquisition/payment process typically happens first?
a. Purchase goods/services.
b. Authorize a purchase.
c. Check vendor credit.
d. Disburse cash.
226. The difference between a purchase requisition and a purchase order is
a. Purchase orders are paper, while requisitions are electronic.
b. Purchase requisitions are electronic, while purchase orders are paper.
c. Purchase requisitions are purely internal documents; purchase orders leave the company.
d. Purchase requisitions often have different prices than purchase orders.
Which of the following is the best example of a conflict of interest?
a. RKH Corporation established a list of preferred vendors.
b. RKH’s conflict-of-interest policy was developed by their auditors.
c. RKH purchases 80 percent of its inventory from a firm where its purchasing agent is a
stockholder.
d. All of the above constitute conflicts of interest.
227. Which documents must be matched before paying a vendor’s invoice?
a. Purchase order, invoice, remittance advice
b. Purchase requisition, invoice, packing list
c. Purchase order, invoice, receiving report
d. Purchase requisition, purchase order, invoice
Which of the following would be represented in a data flow diagram with a line?
a. Prepare purchase order
b. Inventory file
c. Vendor
d. Purchase requisition
228. Which of the following is a form of insurance for employee behavior?
a. Bonding
b. Workers’ compensation insurance
c. Property insurance
d. Life insurance
229. Indicate whether each statement below is (i) always true, (ii)
sometimes true, or (iii) never true. For any statements that are (ii) sometimes true,
explain when the statement is true.
a. A bill of lading is required in the acquisition/payment process.
b. A data flow diagram of the acquisition/payment process has six numbered circles.
c. A vendor invoice triggers a cash disbursement event in a well-organized acquisition/payment
process.
d. Companies without a conflict-of-interest policy have weak internal control over the acquisition/
payment process.
e. Daily bank reconciliations eliminate the need for other forms of internal control over cash.
f. Most of the documents in the acquisition/payment process are paper-based, rather than electronic.
g. Purchase orders are binding contracts between a customer and a vendor.
h. The passage of time triggers events in the acquisition/payment process.
i. The receiving department should have a blind copy of the purchase order.
j. When two signatures are required, blank checks should be signed by one person to promote
operating efficiency.
230. The steps in the sales/collection and acquisition/payment processes
are listed below, but they are out of order. Put the statements in the proper order
based on how they occur in organizations.
a. An operating department in the buying organization requests goods and services.
b. The billing department in the selling organization bills the client.
c. The buying organization’s receiving department receives the goods.
d. The cash disbursements department in the buying organization disburses cash.
e. The cash receipts department in the selling organization collects payment.
f. The credit department in the selling organization approves the customer’s credit.
g. The purchasing department in the buying organization authorizes the purchase.
h. The sales department in the selling organization takes the customer’s order.
i. The selling organization’s shipping department ships the product.
j. The warehouse in the selling organization fills the order based on approved credit.
231. What is the basic purpose of each business process discussed in this chapter (conversion,
financing, human resources)?
What are the similarities and differences between job costing and process costing systems?
How is each system reflected in the organization of the accounting information system?
232. What are the four common transactions associated with the financing business process?
What information must be tracked for each transaction?
What forms are commonly used in processing payroll transactions?
233. How are the purposes of internal control fulfilled in each business process discussed in
the chapter? Indicate whether each of the following types of businesses would be
more likely to use a job or process costing system. Justify your choices.
a. Architect f. Landscaper
b. Attorney g. Magazine publisher
c. Dentist h. Management consultant
d. Heavy-equipment manufacturer i. Pet groomer
e. House painter j. Tax preparer
234. Which business process (conversion, financing, or human resources) is most closely associated with each transaction listed below?
| a. Payroll taxes expense f. Retained earnings
Cash Capital stock b. Manufacturing overhead g. Work in process Accumulated depreciation Manufacturing overhead c. Treasury stock h. Interest expense Cash Premium on bonds payable d. Cash Interest payable Capital stock i. Cash Additional paid-in capital Discount on bonds payable e. Payroll expense Bonds payable Wages payable j. Cost of goods sold Withholding taxes payable Finished goods |
f. Retained earnings
Cash Capital stock b. Manufacturing overhead g. Work in process Accumulated depreciation Manufacturing overhead c. Treasury stock h. Interest expense Cash Premium on bonds payable d. Cash Interest payable Capital stock i. Cash Additional paid-in capital Discount on bonds payable e. Payroll expense Bonds payable Wages payable j. Cost of goods sold Withholding taxes payable Finished goods |
235. Explain what is happening in each transaction presented in
the previous exercise. For example, in transaction ( a ), the company is paying its share
of payroll taxes.
236. Payroll computations and analysis. Eric is the president and chief executive officer of
his own management consulting firm. He has five employees: Jon Jones, Lupe Ban a,
Austin Pei, Diane Driscoll, and Yu Chung Wright. Selected information for each employee is listed in the table below:
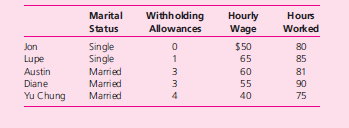
Employees have three kinds of taxes withheld from their wages: federal income,
state income, and Social Security. Social Security is withheld from all employees at
9.75 percent of their gross pay. Single employees have federal income tax withheld at a
base rate of $200 plus $50 for each withholding allowance; married employees’ federal
tax withholding is $150 plus $25 for each withholding allowance. State income tax is
withheld at 30 percent of the federal amount for each employee. Employees are paid
every two weeks and receive 1.5 times their regular hourly wage for any hours in excess
of 80. In addition, Jon and Austin contribute $50 each pay period to an employee pension
fund; Lupe and Diane contribute $75 each pay period for group health insurance.
Using Access or Excel, prepare a payroll register based on the preceding data.
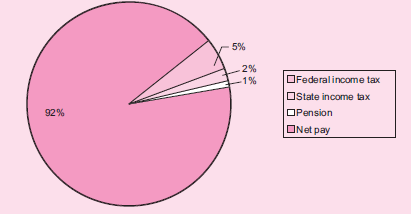
Then, prepare a report for Eric that shows the average gross pay and the average hourly
wage for all five employees. Finally, prepare a pie-chart graph for each employee
showing the breakdown of gross pay into each amount withheld and net pay. (An
example for Jon is shown below.)
237. Several data items that might be included on a payroll form are
listed below on the left. The standard payroll forms discussed in the chapter are listed
below on the right. For each data item, indicate the form(s) on which you’d find it.
a. Address of employee 1. Form 940
b. Employee name 2. Form 941
c. Employer identification number 3. Form 1099
d. Federal income tax withheld 4. Form W-2
e. Location of employer 5. Form W-4
f. Marital status
g. Number of withholding allowances
h. Social Security number
i. State income tax withheld
j. Unemployment tax paid—federal
238. Please complete the puzzle below using terminology from the
chapter.
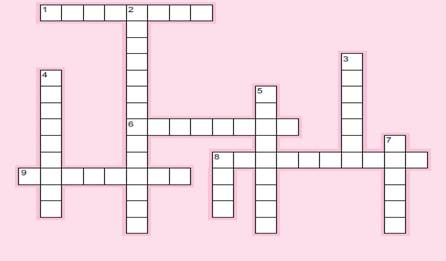
Across
1. Factory equipment depreciation classification.
6. Risk associated with financing process.
8. One of three business processes discussed in the chapter.
9. One type of dividend.
Down
2. One of three business processes discussed in the chapter.
3. Costing system for undifferentiated goods.
4. What many companies do with payroll processing.
5. One of three business processes discussed in the chapter.
7. Stated interest rate on long-term debt.
8. Method used for most treasury stock transactions.
239. Please match each item on the left with the most appropriate item on the
Right
1. Custom-made bicycles a. Associated with dividend payments
2. Date of record b. Human resource process internal control
3. Direct material c. Internal control for missed payments
4. Electronic funds transfer d. Job costing product
5. Factory supplies e. Method for gathering data
6. Number of interest payments f. Needed for stock issuance transaction
7. Observation g. Overhead
8. Par value of a share h. Process costing product
9. Pencils i. Required data for long-term debt transactions
10. Time clock j. Steel, for an automobile
240. The after-tax cost of debt would be most closely associated with the _____ process.
a. Conversion
b. Human resource
c. Financing
d. Bookkeeping
A company that reproduces fine works of art, such as the Mona Lisa, would most likely use
what kind of production process?
a. Hybrid
b. Conversion
c. Job
d. Process
241. A journal entry in a company’s accounting information system debited retained earnings.
The purpose of the journal entry is most likely
a. To record the declaration of a cash dividend.
b. To account for the sale of finished goods inventory.
c. To apply manufacturing overhead.
d. To account for an employee leasing arrangement.
242. TRN Corporation produces a product that is highly perishable. Which of the following
internal controls is the best alternative for controlling the risk of product spoilage?
a. Separation of duties
b. Adequate documentation
c. Employee training
d. Specialized storage containers
243. Whadda Ya Know University recently discovered that one of its professors had falsified his
educational transcripts and does not actually hold any college degree. Which of the following
constitutes an appropriate corrective control in this situation?
a. Background checks
b. Well-established performance evaluation procedures
c. Termination
d. All of the above
Forced vacations
a. Are irrelevant in most companies, as employees are eager to take vacations.
b. Can reveal fraudulent activities.
c. Violate federal employment laws.
d. Save a company money.
244. A production cost report
a. Is most applicable to process costing systems.
b. Is most applicable to job costing systems.
c. Is one of the general purpose financial statements for manufacturers.
d. Originates in the warehouse.
An independent contractor is most closely associated with which of the following forms?
a. 940
b. 941
c. W-2
d. 1099
245. In a DFD of the human resources business process, “evaluate employees” would be represented
with a
a. Line.
b. Circle.
c. Rectangle.
d. Triangle.
RKH Corporation maintains its job costing system using a relational database. Which of
the following pieces of information would not be stored in a table in their system?
a. Total cost of Job A244
b. Manufacturing employee names
c. Department affiliations of each employee
d. Location of manufacturing equipment.
246. Indicate whether each statement below is (i) always true,
(ii) sometimes true, or (iii) never true. For statements that are (ii) sometimes true,
explain when the statement is true.
a. All five business processes discussed in the text are required to create value for stakeholders.
b. Companies with long-term debt establish sinking funds.
c. Conversion process forms are paper-based.
d. Individual units of product in a process costing system are homogeneous.
e. Information technology eliminates the problem of accounts receivable lapping.
f. Separation of duties can be applied to fixed assets used in the conversion process.
g. The “date of record” determines who receives dividends on capital stock.
h. The par value of a share of capital stock is determined by the stock market.
i. The total cost of a batch of units should be calculated and stored in a relational database table.
j. With respect to long-term debt, the “coupon interest rate” and the “market interest rate” are
two ways of referring to the same thing.
247. Define business process management in your own words. Explain why BPM can be considered
part of accounting information systems.
List seven generic steps involved in many BPM projects.
List and discuss seven fundamental principles to keep in mind when undertaking a BPM initiative.
248. How can information technology, flowcharting, and activity-based management come into
play in BPM?
Summarize the three BPM cases discussed in the chapter.
In a format specified by your instructor, respond to the questions for this chapter’s “AIS in
the Business World.”
249. BLZ Corporation designs and produces massively multiplayer
online role-playing games (MMORPG). Designing a completely new game can
take up to two years, while expanding an existing game usually takes 8 to 10 months.
Some of BLZ’s activities, with approximate costs, are shown below:
• Beta testing new games, $2,400
• Developing content for expansions, $7,680
• Fixing software bugs, $16,470
• Manufacturing game software CDs, $50,625
• Marketing and advertising, $7,000
• Processing returned CDs, $3,800
• Responding to player questions, $1,900
• Shipping CDs to retail stores, $8,100
• Writing instructional manuals, $4,200
• Recording transactions in the accounting information system, $9,430
a. Use a four-point scale to categorize the value added by each process, where “1” stands for an
activity with little or no value and “4” stands for an activity with very high value.
b. Prepare a pie chart that shows the percentage of cost in each category.
c. Consider at least two activities you classify as having the lowest value. For each activity, suggest at least two ways it could be improved. Explain your reasoning.
250. Crossword puzzle.
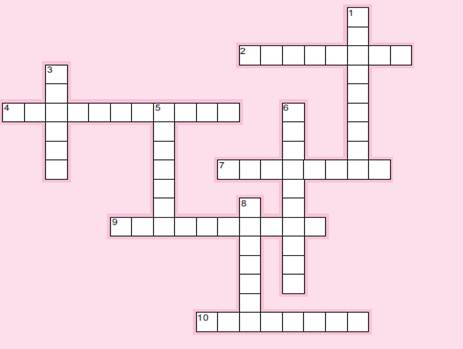
Across
2. Software that can be used in BPM.
4. Should be used cautiously in BPM, and always with well-defined outcomes.
7. -based management is one tool for BPM.
9. Must be defined at the start of a BPM project.
10. The “B” in BPM.
Down
1. The “M” in BPM.
3. BPM is fundamentally about .
5. BPM minimizes or eliminates processes that don’t do this (two words).
6. Purpose of internal control closely related to BPM.
8. The “P” in BPM.
251. Terminology. Please match each item on the left with the most appropriate item on the
right.
1. Best motivation for starting BPM a. Activity-based management
2. Essential element of all BPM projects b. Boundaries
3. Focuses on eliminating waste c. Communication
4. How an organization competes in its markets d. Consultants
5. Internal control purpose associated with BPM e. Efficiency
6. Must be defined before starting a BPM project f. Information technology
7. Often used in, but not essential to, BPM g. Non-value-added activities
8. Should be frequent in BPM h. People
9. Should be reduced or eliminated i. Stakeholders’ needs
10. Should be used cautiously in BPM j. Strategy
252. Business process management can be defined as
A business improvement strategy based on documenting, analyzing, and and redesigning
processes for greater performance.
b. A method of efficiently aligning an organization with the wants and needs of clients.
c. Both A and B.
d. Neither A nor B.
253. The first step in many BPM projects is selecting a process and defining its boundaries.
Which of the following is the best example of a well-defined process?
a. Keeping clients happy
b. Motivating employees
c. Producing goods
d. Issuing capital stock
254. The fourth step in many BPM projects is analyzing data, which could be accomplished with
a. A flowchart.
b. A value-added study.
c. An analysis of the organization’s strategy.
d. The FASB Conceptual Framework.
255. Which of the following is the best example of a BPM project that promotes strong internal
control?
a. Developing an online order-taking process
b. Drawing a flowchart of a company’s new production process
c. Hiring an external consultant to make recommendations about internal control
d. Increasing supervision over employees
256. Accountants can be involved in business process management through
I. Documenting processes.
II. Designing process inputs and outputs.
III. Auditing.
a. I and II only
b. II and III only
c. I and III only
d. I, II, and III
257. Business processes should support
a. Organizational strategy.
b. Top management.
c. Information technology.
d. Employees.
258. All of the following are elements of a value-added activity except
a. A customer is willing to pay for it.
b. It involves a transformation of a process or activity.
c. It is performed correctly the first time.
d. It involves information technology.
259. Which of the following statements is most true?
a. Organizations that use activity-based costing must use activity-based management.
b. An organization must implement activity-based management before it can implement
activity-based costing.
c. Organizations that use activity-based management are likely to use activity-based costing
as well.
d. Activity-based management is the best way to manage business processes.
260. Examples of value-added activities include
I. Ordering raw materials.
II. Testing product quality.
III. Fueling delivery trucks.
a. I and II only
b. I and III only
c. II and III only
d. I, II, and III
Which of the following generic BPM steps occurs first?
a. Analyze process-related data.
b. Collect process-related data.
c. Identify potential improvements.
d. Optimize the process.
261. Indicate whether each statement below is (i) always true,
(ii) sometimes true, or (iii) never true. For those that are (ii) sometimes true, explain
when the statement is true.
a. Information technology is an important part of business process management projects.
b. “Value added” is defined by external customers.
c. External consultants are always necessary for successful BPM projects.
d. A process can be value added if it helps employees work more efficiently.
e. Fixing product defects is not a value-added activity.
f. Many forms of information technology can be used in managing business processes.
g. Business processes are only value added if external customers are willing to pay for them.
h. A service-based business has more opportunities for BPM projects than a manufacturing
business.
i. Managing business processes requires critical thinking and judgment.
j. Data flow diagrams are less useful than flowcharts in managing business processes
262. What four common classifications are often associated with computer crime?
What computer crime–related risks and threats are associated with information systems?
What categories are commonly associated with computer criminals? Describe each category.
263. How can organizations safeguard against computer crime? How can they detect it and recover
from it if it happens? What role does CoBIT play in those tasks? What is CoBIT? What are the seven information criteria discussed in the CoBIT framework?
Respond to the questions for this chapter’s “AIS in the Business World.”
264. What would motivate someone to engage in computer crime?
Choose one of the AICPA Top Ten Technologies and explain how it might be used to engage in computer crime.
Suggest at least three specific internal controls you’d employ to prevent, detect, or correct the
computer crime you identified above.
265. Brad Willman contributed to the arrest of several pedophiles in Canada and the United
States. But he collected evidence for his investigation by hacking into others’ computers.
Read about this case in Cori Howard, “Internet Vigilante,” Maclean’s (June 6, 2005). What
model of ethics, discussed in Chapter 3, best describes Willman’s actions? Were Willman’s
actions ethical? What legal action, if any, should be taken against Willman?
266. Which element(s) of Carter’s taxonomy apply to each of
the following situations? If more than one category applies, explain why.
a. A bookkeeper steals cash as it comes into the company. The bookkeeper later falsifies
accounting entries using general ledger software to cover the trail.
b. A bored teenager initiates a denial-of-service attack on his Internet service provider’s information
system.
c. A disgruntled employee uses a previously installed “back door” into an information system
to lock out other users by changing their passwords.
d. A gang of criminals breaks into a local retail store. They steal all the store’s computers and
then later hack into them for the purpose of identity theft.
e. A pair of computer criminals uses e-mail to contact victims for an illegal pyramid scheme.
They use money from new investors, rather than profits, to pay off old investors, keeping
most of the money themselves.
f. A recently fired employee laid the groundwork for corporate espionage by installing spyware
on the company’s network.
g. A student discovers the password to his university’s information system. He then hacks the
system to change grades for himself and his friends.
h. A woman impersonates her wealthy employer, stealing personal information about the
employer from her bank’s information system.
267. Which type(s) of business risks/threats described
in the chapter best applies to each situation below? If more than one applies, explain why.
a. Blackmail based on stolen information.
b. Concurrent attacks against a determined target.
c. Digital graffiti.
d. Discovery of customer Social Security numbers by external parties.
e. Hacking.
f. Intentional modification of information.
g. Mistakes in data entry.
h. Power failure.
i. Salami technique.
j. Stealing research and development data for new products.
k. Trojan horse.
268. Fill in the blanks below with appropriate terms
related to the types of computer criminals discussed in the chapter.
a. ———represent the largest threat to a company’s information systems and underlying computer
infrastructure.
b.————- has been getting into spamming, phishing, extortion, and all other profitable branches
of computer crime.
c.———- could seriously disrupt power grids, , ————–transportation, and others if they were
to exploit vulnerabilities to disrupt or shut down critical functions.
d. A ———-describes a young inexperienced hacker who uses tools and scripts written by others
for the purpose of attacking systems.
e. Corporate——— have begun turning to———- techniques to gather the information they
desire.
f. Cyber-criminals possess———– and have turned to hacking, not for the———- but for the———.
.
g. The term hacker originally described someone who wanted to———- of computers and
attempted to———– to the limit.
269. Classify each of the following controls as physical, technical,
or administrative. Then, describe each control in your own words.
a. Access control software
b. Adequate supervision of employees
c. Badges
d. Encryption
e. Firewalls
f. Internal audits
g. Intrusion detection systems
h. Locks
i. Ongoing training regarding security issues
j. Security guards
k. Security policy
l. Smoke detectors
m. Universal power supplies
270. Indicate which of the CoBIT information criteria are violated
in each of the following independent scenarios. Justify your choices.
a. Financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2008, are completed and published in
June 2009.
b. A company with $1 million in annual revenues maintains an accounting information system
with paper journals and ledgers.
c. Employee names, identification numbers, job classifications, and addresses are posted on a
company Web site.
d. A careless employee spilled a soft drink on a file server. The server was damaged and could
not be used for three days.
e. The CEO and CFO fail to provide the documents required by the Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
271. The C-I-A triad contains three elements: confidentiality, integrity, and
availability. Refer back to one or more of the professional codes of ethics discussed in
the first part of the text. How are the elements of the ethical code(s) you selected
related to the triad? For example, confidentiality and integrity are explicitly mentioned
in the IMA code of ethics.
272. Crossword puzzle. Please complete the puzzle below using terminology from the
Chapter.
Across
7. Developed a four-part taxonomy for computer crime.
8. Another name for technical security controls.
10. Type of computer crime that exploits weak internal controls.
Chapter 15 Computer Crime and Information Technology Security 307
Down
1. Element of the C-I-A triad that refers to timely access to necessary information.
2. The most precious asset of most organizations.
3. Type of behavior associated with service interruptions and delays.
4. For many hackers, fraud is this type of crime.
5. Key component of an organization’s information security management system.
6. Control type concerned with identifying unwanted events.
9. A type of malicious software that reproduces over a network.
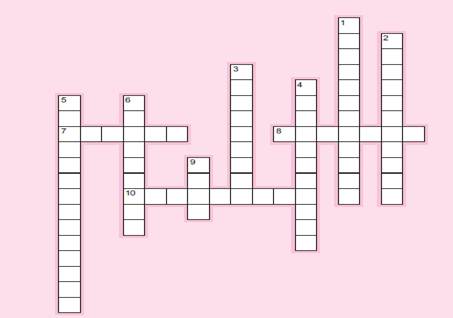
273. Please match each item on the right to the most appropriate item on the left.
| 1. Confidentiality
2. Creating fake refunds to benefit a friend 3. Data diddling 4. Human element 5. Incidental 6. Instrumentality 7. Logic bomb 8. Salami technique 9. Sarbanes-Oxley Act 10. Willful neglect |
a. Computers used to carry out a crime.
b. Crime classification that does not necessarily require a computer. c. Data are protected from unauthorized disclosure. d. Designed to help restore consumer confidence. e. Information manipulation. f. Intentionally changing information in a system. g. Interest of less than one cent diverted to computer criminal’s account. h. Most vulnerable part of an information system. i. One type of service interruption/delay. j. Shuts down a payroll system if a specific employee number is deleted. |
274. The name most closely associated with a taxonomy of computer crime is
a. Sarbanes.
b. Oxley.
c. Legault.
d. Carter.
Computer crime has been defined as any illegal act for which knowledge of is used to
commit the offense.
a. Database software
b. Hacking techniques
c. Computer technology
d. Spamming
275. Which of the following is most closely associated with a computer worm?
a. Sapphire
b. Online gambling
c. Organized crime
d. All of the above are associated with computer worms.
Which of the following is not a type of computer criminal?
a. Script kiddie
b. Hacker
c. Salami criminal
d. Terrorist
276. Administrative security controls include
a. Management constraints.
b. Operational procedures.
c. Accountability procedures.
d. All of the above.
The CoBIT framework includes information criteria.
a. Three
b. Four
c. Seven
d. Some other number
277. Which of the following is not a domain in CoBIT?
a. Prevent and correct
b. Plan and organize
c. Acquire and implement
d. Monitor and evaluate
In CoBIT, accountability flows downward from
a. External auditors to internal auditors.
b. The audit committee to internal auditors.
c. Stockholders to the audit committee.
d. Stakeholders to the board of directors.
278. Which of the following uses an algorithm to secure information transmitted between
computers?
a. Password rotation
b. Firewalls
c. Encryption
d. Security audit
279. In CoBIT, which of the following flows upward from the board of directors to stakeholders?
a. Financial and internal control disclosures
b. Accountability
c. Disclosures regarding information governance control
d. All of the above
280. Indicate whether each of the following statements is (i) always
true, (ii) sometimes true, or (iii) never true. For those that are (ii) sometimes true,
explain when the statement is true.
a. A specific instance of computer crime can involve multiple categories from Carter’s
taxonomy.
b. Computer crime involves using a computer to commit a crime.
c. Computer crime is perpetrated by organized crime groups.
d. Confidentiality, availability, and data integrity comprise the C-I-A triad.
e. Each element of the C-I-A triad is also mentioned in CoBIT’s information criteria.
f. Hackers may be motivated by profit or by entertainment.
g. Information technology controls can be physical, technical, or administrative.
h. Organizations that implement CoBIT are immune to computer crime.
i. Perpetrators of computer crime come from outside the organization.
j. The “salami technique” is an example of information manipulation.
281. What is information overload? What causes it? What are its effects? How can decision makers deal with information overload in their professional lives?
282. Explain the idea of knowledge management. Why is it important? What are some techniques you can use to manage knowledge now and in the future?
283. Summarize the ideas and steps associated with Wolcott and Lynch’s Steps for Better Thinking. Prepare a response to the questions for this chapter’s “AIS in the Business World.”
284. Consider the list of current and classic issues
in accounting presented below (or others specified by your instructor). With your
instructor’s help and guidance, form a team of students to investigate one of the issues.
Use the Steps for Better Thinking to analyze the issue and prepare a short oral report
for the class.
a. What are the obstacles associated with adopting International Financial Reporting Standards?
b. Should the provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act be extended to nonpublic corporations?
c. Will principles-based accounting become the norm for U.S. GAAP?
d. Has the 150-hour requirement for becoming a CPA been a success?
e. What systems documentation techniques should be taught in AIS courses?
f. Has the conceptual framework of accounting fulfilled its purpose?
g. What issues should managers consider with regard to corporate governance?
h. Should social and environmental reporting be mandatory?
i. How, if at all, should fair-value accounting be implemented?
285. Point your Web browser once again to www.download
.com . Search for knowledge management software; choose one example and prepare a
short oral report for the class on its capabilities and cost.
286. making and knowledge management system. Based on what you’ve
learned in this chapter, prepare a brief written report that summarizes your personal
plan for making better decisions and managing knowledge. Use a specific example of
a recent past or upcoming decision to illustrate your decision-making model.
287. Please complete this puzzle using appropriate terminology from the chapter.
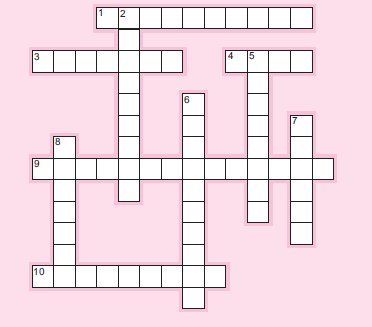
Across
1. Creating a knowledge—————– is one purpose of knowledge management systems.
3. Error type that describes repeating past ineffective behaviors.
4. Number of SBT levels after the foundation.
9.————– design: one cause of information overload.
10. Type of information analysis that may result from information overload.
Down
2. SBT level focused on interpreting and organizing information.
5. Occurs when too much information comes in too quickly.
6. Task and process————- : a cause of information overload.
7. Along with visual aids, can help combat information overload.
8. Author who believed that knowledge may be the only economically sustainable resource.
288. Please match each item on the left with the most appropriate item on the right.
1. Wolcott and Lynch a. A system for creating value from intellectual assets
2. Satisficing b. Software that can be used to implement a KMS
3. Relapse errors c. Human tendency to rely on rules for making decisions
4. Prioritizing d. Looking at information from multiple points of view
5. Knowledge management e. SBT step that involves identifying personal bias
6. Identifying f. Simon’s notion that people will accept the first
reasonable solution for a problem
7. Exploring g. Starting place for Steps for Better Thinking
8. Envisioning h. Tendency to make the same mistakes repeatedly
9. Bounded rationality i. The creator(s) of Steps for Better Thinking
10. Database i. The creator(s) of Steps for Better Thinking
289. Which of the following types of information is most likely to create information overload
for an experienced accountant?
a. Elements of financial statements
b. Tax pronouncements
c. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act
d. Rules of debit and credit
The Gunning Fog Index is most closely related to
a. Task and process parameters.
b. Information characteristics.
c. Organizational design.
d. Personal factors.
290. Which of the following statements about Steps for Better Thinking is most true?
a. Using the steps effectively requires a college degree as a precursor.
b. SBT is the best model for decision making available to accountants today.
c. Each step requires more complex tasks than the steps that precede it.
d. SBT is most applicable to ethical decision-making situations.
A group of accounting students told their accounting professor to “give them the right
answer to a problem so they could memorize it for the exam.” The students were exhibiting
a. Satisficing.
b. Bounded rationality.
c. Relapse errors.
d. Good knowledge management skills.
291. Knowledge should be managed as a(n)
a. Asset.
b. Element of shareholders’ equity.
c. Liability.
d. Source of revenue.
Which of the following is not a cause of information overload?
a. Personal factors
b. Relapse errors
c. Information technology
d. Task and process parameters
292. Which element of Steps for Better Thinking focuses on dealing with limitations of problem
solutions?
a. Identifying
b. Exploring
c. Prioritizing
d. Envisioning
The concepts discussed in this chapter can be applied to
a. Evaluating software for an accounting information system.
b. The job search process.
c. Studying for professional exams.
d. All of the above.
293. Which of the following is not an effective way to deal with information overload?
a. Leave important decisions to others.
b. Define decision models and rules for common decision contexts.
c. Focus on creating value-added information.
d. Formalize the language used to describe information.
Who first suggested the ideas of satisficing and bounded rationality?
a. Drucker
b. Wolcott
c. Simon
d. Pacioli
294. Indicate whether each of the following statements is (i) always
true, (ii) sometimes true, or (iii) never true. For those that are (ii) sometimes true,
explain when the statement is true.
a. A supportive organizational culture is an important step in knowledge management.
b. Bounded rationality prevents people from making good decisions.
c. Breaking up a complex job into smaller tasks can help combat information overload.
d. Even the smartest human beings have a limited capacity for processing information.
e. Information characteristics can contribute to information overload.
f. Information technology is a cause of information overload.
g. Information technology is a solution for information overload.
h. Knowledge management systems involve relational database software.
i. The levels of Steps for Better Thinking involve increasingly complex tasks.
j. Visual maps resemble data flow diagrams.
295. What are the benefits of obtaining professional certification?
What three common components are associated with most professional certifications in
accounting?. Describe the content and process associated with taking one or more of the professional
exams discussed in the chapter. Respond to the questions for this chapter’s “AIS in the Business World.”
296. As an undergraduate, I had a friend named Gary. Although
he started off as an accounting major (like me), he changed to a computer-related
field after one semester. When I asked him why, he said, “By the time we graduate,
all accountants will have been replaced by computers.” I don’t know what happened
to Gary after we left college, but, clearly, his prediction didn’t come true. Use the
concepts discussed in the chapter to explain why it’s unlikely all accountants will
ever be replaced by computers.
297. Visit your campus career center; talk with a
career counselor about your future career plans. Take an aptitude or interest assessment,
such as the Discover Inventory or Strengths Quest; what does the assessment tell
you about yourself? Map out a tentative plan for your accounting career, starting with
earning your accounting degree.
298. Choose one of the professional associations discussed in the chapter.
Attend a meeting of a local chapter; talk with professionals in the field about their job
responsibilities and the costs and benefits of certification. Prepare to share your findings
with your classmates as directed by your instructor.
299. Choose one of the four certifications discussed in the chapter. Consider its exam requirements in light of your accounting curriculum; which accounting courses are particularly relevant in preparing for the exam? (Don’t limit yourself to accounting courses alone here—consider the totality of your degree, including general education.)
300. Summarize the ethical code of one of the four professional organizations discussed in the
chapter. Prepare a short oral presentation of your summary for the class.
Through research or your own imagination, identify a situation in which an accountant
would have to consult the ethical code you summarized in ( a ). Write a one-page case study
of the situation and explain how it should be resolved under the appropriate set of ethical principles.
301. Research the requirements to become a Certified Public Accountant in
your state. Prepare a brief oral or written report discussing your findings. Start your
research at www.nasba.org ; also visit www.cpa-exam.org for details of the CPA
exam.
302. Please complete the crossword puzzle below using appropriate terminology
from the chapter.
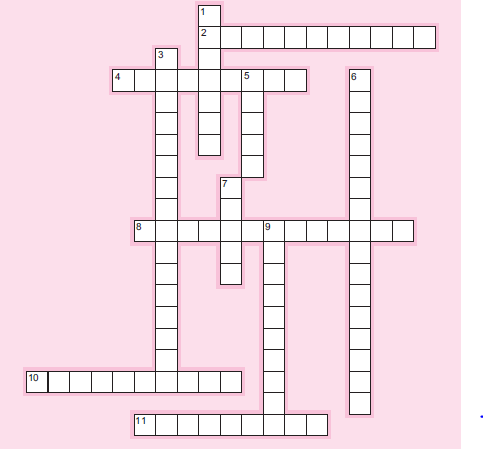
Across
2. One of three parts of a generalized certification process.
4. One of three parts of a generalized certification process.
8. An important piece of legislation tested on many certification exams.
10. One way to research employment opportunities.
11. Try to achieve this when it comes to certification and your career interests.
Down
1. Holland’s :———- a tool that classifies employment environments in six categories.
3. One of the four parts of the CMA exam.
5. The sponsoring organization for CISAs.
6. An exam topic common to many accounting certification exams.
303. Legal elements of :———– one of the areas tested on the CFE exam.
9. One of three parts of a generalized certification process.
Match each item in the left column with the best item in the right column.
1. A certification exam given online a. Career mission statement
2. A short, simple statement that explains how you b. Certified Fraud Examiner
expect to create value for a prospective employer
3. A topic tested on the CFE exam c. Certified Information Systems Auditor
4. A topic tested on the CISA exam d. Experience
5. A topic tested on the CMA exam e. Financial transactions
6. Number of career options available with most f. Investigative
accounting certifications
7. Number of elements in most certification processes g. Protection of information assets
8. One element of Holland’s hexagon h. Strategic management
9. Other than exams and education, a common element i. Three
of certification
10. Professional exam given “in person” j. Unlimited
304. Which of the following is common to all four certifications discussed in the chapter?
a. They are globally recognized.
b. They require professional experience.
c. Both of the above.
d. None of the above.
The common components associated with professional accounting certification are
a. Education, experience, and oral examination.
b. Ethics, education, and experience.
c. Education, experience, and examination.
d. Graduate-level education, ethics, and experience.
305. Which professional exams are given in an entirely online environment?
a. CMA and CISA
b. CISA and CFE
c. CMA and CFE
d. CISA and CIA
Which of the following statements is most true?
a. All accountants should become CPAs.
b. Professional certification really isn’t necessary if you have a master’s degree.
c. Most accounting certifications require at least some knowledge of accounting information
systems.
d. Earning a given certification, such as the CMA, locks a professional into a very specific
career.
306. Which of the certifications discussed in the chapter covers the broadest range of topics?
a. CFE
b. CMA
c. CISA
d. CIA
The difference between a “license” and a “certificate” is
a. A certificate is issued by a state; a license is issued by a federal agency.
b. A license is issued by a state; a certificate is issued by a federal agency.
c. A license confers permission; a certificate demonstrates knowledge.
d. A certificate confers permission; a license demonstrates knowledge.
307. Which of the following is common to all four certifications discussed in the chapter?
a. They are globally recognized.
b. They require professional experience.
c. Both of the above.
d. None of the above.
The common components associated with professional accounting certification are
a. Education, experience, and oral examination.
b. Ethics, education, and experience.
c. Education, experience, and examination.
d. Graduate-level education, ethics, and experience.
308. Which professional exams are given in an entirely online environment?
a. CMA and CISA
b. CISA and CFE
c. CMA and CFE
d. CISA and CIA
Which of the following statements is most true?
a. All accountants should become CPAs.
b. Professional certification really isn’t necessary if you have a master’s degree.
c. Most accounting certifications require at least some knowledge of accounting information
systems.
d. Earning a given certification, such as the CMA, locks a professional into a very specific
career.
309. Which of the certifications discussed in the chapter covers the broadest range of topics?
a. CFE
b. CMA
c. CISA
d. CIA
The difference between a “license” and a “certificate” is
a. A certificate is issued by a state; a license is issued by a federal agency.
b. A license is issued by a state; a certificate is issued by a federal agency.
c. A license confers permission; a certificate demonstrates knowledge.
d. A certificate confers permission; a license demonstrates knowledge.
310. Please indicate whether each of the following statements is
(i) always true, (ii) sometimes true, or (iii) never true. For those that are (ii) sometimes
true, explain when the statement is true.
a. A professional resume should be limited to a single page.
b. Accounting information systems topics are important in most certification exams.
c. Certification leads to higher salaries.
d. Certifications in accounting require two years of working experience.
e. Fraud investigators have earned the Certified Fraud Examiner credential.
f. Professional certification exams are given online.
g. Professional resumes should use action verbs like “coordinated” and “implemented.”
h. Successful accountants have a Holland code of CSI.
i. The purpose of earning an accounting degree is to become a CPA.
j. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 can be tested on any accounting professional exam.
311. List and discuss the seven types of audits described in the chapter.
Explain the 10 generally accepted auditing standards that guide financial audits.
Describe the common steps associated with an audit. Prepare a response to the questions for this chapter’s “AIS in the Business World.”
312. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
conjures up images of rockets and voyages to the stars. And all its research and operations
require a fairly sophisticated, detailed accounting information system. When
NASA’s 2003 financial statements and accounting information system were audited
by PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC), the CPA firm issued a disclaimed audit opinion.
According to Frieswick, “PwC complained that NASA couldn’t adequately document
more than $565 billion in year-end adjustments to the financial-statement accounts,
which NASA delivered to the auditors two months late.” NASA’s chief financial
officer, Gwen Brown, testified before a congressional committee in May 2004 about
$2 billion it could not trace through the AIS. “In her testimony, Brown assured subcommittee
members that the missing $2 billion was not the result of ‘fraud, waste or
abuse.’ But when pressed on what did cause the money to go missing, she admitted the
agency wasn’t sure.” NASA’s inspector general, Robert Cobb, talked about problems
with the implementation of the agency’s new AIS. He believed NASA wouldn’t get a
clean audit opinion until at least 2007.
a. What elements of an accounting information system are evaluated in an audit?
b. What are the processes and attitudes associated with an audit?
c. What types of audits are involved in professional accounting?
d. List and describe the four types of opinions associated with financial statement audits.
313. Consider the list of internal controls discussed in this chapter
(e.g., security checks on personnel, controlled access, and data encryption). Choose
one control from each category (administrative, physical, and technical). Prepare an
oral and/or written report that describes its nature and importance in the accounting
information system
314. What type of audit is indicated in each of the following situations?
a. Checking internal controls over the sales/collection process.
b. Determining how an employee embezzled cash.
c. Establishing whether an audit conformed to all provisions of Sarbanes-Oxley.
d. Evaluating the accounting policy choices management made for conformity with GAAP.
e. Expressing an opinion on the fairness of a company’s financial statements.
f. Inputting sample transactions and verifying the output from Peachtree.
g. Observing internal controls over inventory to improve process effectiveness.
h. Performing a comprehensive analysis of an Italian firm’s accounting information system.
i. Using test data to determine how QuickBooks processes transactions.
j. Validating the assumptions made for a major capital investment.
315. Which of the 10 standards is violated in each of the following
independent situations? Some situations may violate more than one.
a. A team of auditors, each with varying levels of experience, divided up the audit tasks and
completed them independently before expressing an opinion on the statements.
b. An audit client changed its inventory cost flow assumption from LIFO to FIFO in the last
year. The audit opinion makes no mention of the change.
c. Auditors relied solely on the client’s assertions in evaluating account balances.
d. Austin supervised the audit team for a company in which he has an investment.
e. Chip relied solely on the client’s assessment of its AIS integrity in determining compliance
tests for an audit.
f. Sebastian conducted his first audit during his last semester of college. He audited the
accounting information system of a nonprofit organization where he volunteers.
316. Fill in the blanks in each statement below with appropriate terminology
to describe the generic steps in a financial statement audit. Then, put the steps
in the correct order.
a. Assess integrity.
b. Evaluate management’s .
c. Issue the .
d. Perform testing.
e. Review the system.
317. Use appropriate terminology from the chapter to complete the puzzle below.
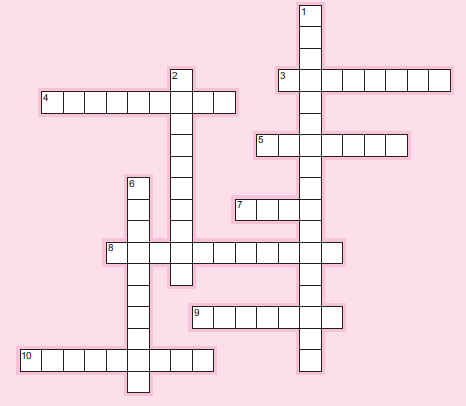
Across
3. A common aspect of all types of audits.
4. The group of GAAS with the most individual elements.
5. One of the three groups of auditing standards.
7. Certification most closely associated with a systems audit.
8. Audit type that examines business processes for reasonableness.
9. An audit opinion that indicates statements are not presented in accordance with GAAP.
10. Audit type that results in an opinion on statements.
Down
1. Starting point for a fraud audit.
2. One of the groups of GAAS.
6. Audit type that relies on the Yellow Book.
318. Please match each item on the left with the most appropriate item on the right.
1. Bank reconciliation a. A “clean” opinion
2. Compliance b. Field work standard
3. Disclosure c. General standard
4. Flowcharting d. Important in international audits
5. GAAP e. Internal control example
6. Independence f. Reporting standard
7. Internal control g. Standard associated with financial statement audits
8. Laws and religion h. Systems documentation technique often used in
operational audits
9. Target i. Type of audit most closely associated with
governmental entities
j. Ultimate subject of an investigative audit
10. Unqualified
319. Which type of audit requires the broadest knowledge of nonfinancial issues?
a. Financial
b. Investigative
c. Compliance
d. International
Which of the following information sources would you consult first in an investigative audit?
a. Target
b. Co-conspirators
c. Documents
d. Neutral third-party witnesses
320. Which of the following is not a classification associated with generally accepted auditing
standards?
a. Information technology
b. Field work
c. Reporting
d. General
An ERP system could be associated with audits.
a. Systems
b. Financial
c. Investigative
d. All of the above
321. In a financial audit, which of the following can someone assume is adequate unless specifically
told otherwise?
a. Consistency
b. Disclosure
c. Internal controls
d. All of the above
In an investigative audit, co-conspirators are interviewed before the target
a. Because the information they can provide is more important.
b. So the investigative auditor will be certain to get a confession from the target.
c. Because they can be offered a “deal” that will help prove the fraud.
d. Because they are younger.
322. Which of the following is not associated with field work standards?
a. Supervision
b. Internal control
c. Evidence
d. Risk management
Which type of audit opinion ensures that financial statements are true and correct?
a. Unqualified
b. Qualified
c. Both of the above
d. None of the above
323. The standard for government audits is
a. The Yellow Book.
b. SAS 70.
c. COSO’s internal control framework.
d. SOX.
As part of their annual reports, SOX-compliant organizations must discuss the scope and
adequacy of internal controls. That requirement comes from section
a. 302.
b. 401.
c. 404.
d. 802.
324. Determine whether each of the following statements is (i) always
true, (ii) sometimes true, or (iii) never true. For those that are (ii) sometimes true,
explain when the statement is true.
a. A disclaimed audit opinion means the financial statements contain errors.
b. Audits focus on a company’s financial statements.
c. Field work standards contain guidelines for conducting an audit.
d. Financial statement audits result in an unqualified opinion.
e. Following the provisions of Sarbanes-Oxley, CEOs can delegate their responsibility to examine
internal controls.
f. In an investigative audit, the target should be interviewed first.
g. Independent auditors in the United States help determine whether financial statements are true.
h. Investigative audits examine five main assertions about financial statements.
i. U.S. companies need to undergo annual financial statement audits.
j. Weak internal controls lead to qualified audit opinions.

