Assume a 2-D scenario in which a pellet filled with radiotracer is located at the origin. The pellet emits gamma rays in the x-y plane and its radioactivity is A = 0.54 mCi as shown in Figure P8.7(a). The detector is made of a material with μ = 0.64 cm−1 and thickness of b = 2 cm.
(a) What is the average rate of photons per second hitting the detector (in photons per second)?
(b) Find the efficiency of the detector at its center (that is, at x = 0). A parallel hole collimator with septal thickness h = 2.5 mm, septal height l = 8 cm, and hole diameter d = 5 mm is added onto the detector, as shown in Figure P8.7(b).
(c) What is the collimator resolution RC?
(d) Assume the intrinsic resolution of the detector is 1 mm. What is the overall PSF of the camera knowing that both hC and hI are Gaussian?
(e) Given the geometry, how many holes receive radiation that can hit the detector?
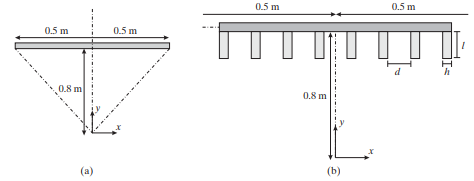
Figure P8.7 (a) Detector without collimator. (b) Detector with collimator. See Problem 8.17.
(f) If l gets larger, at some point radiation will only be able to hit the detector through one hole. Find the smallest l = l0 when this happens. What is Rc in this case?
(g) If the camera sensitivity is ![]() when l = 8 cm, what is its sensitivity when l = l0? (For simplicity assume that the effective height of a collimator hole is equal to l.
when l = 8 cm, what is its sensitivity when l = l0? (For simplicity assume that the effective height of a collimator hole is equal to l.

