Consider a 2-D object consisting of two triangle compartments, as shown in Figure P9.4. Suppose a solution containing a 511 KeV gamma ray emitting radionuclide with concentration f = 0.5 mCi/cm3 fills the lower triangle. The linear attenuation coefficients in the two regions are μ1 = 0.1 cm−1 and μ2 = 0.2 cm−1. Assume perfect detection in all cases and ignore the inverse square law effect.
(a) We image the radioactivity using a 2D SPECT scanner. Compute the projected radioactivities gSPECT(![]() , 0◦) and gSPECT(
, 0◦) and gSPECT(![]() , 180◦). The camera is located on the +y-axis looking down when θ = 0◦.
, 180◦). The camera is located on the +y-axis looking down when θ = 0◦.
(b) Now assume the radionuclide in part (a) is replaced by a positron emitting radionuclide with the same concentration. Assume the linear attenuation coefficients in the two regions are the same as in part (a). If using a 2D PET scanner, compute gPET(![]() , 0◦) and gPET(
, 0◦) and gPET(![]() , 180◦).
, 180◦).
(c) Explain why attenuation is not a big problem in PET.
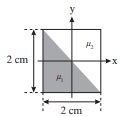
Figure P9.4 An object with triangular compartments. See Problem 9.4.

